
|
|
THEORY: A scientifically verified, interrelated body of general principles, axioms, and assumptions that is used to explain and understand real world phenomena. Theories are the cornerstone of the scientific method. They generate the hypotheses that are verified against real world data, which is the day-to-day process of doing science. The construction and refinement of theories, accomplished through the hypothesis verification process, is also the basic goal of doing science.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           TWO-SECTOR, TWO-MARKET CIRCULAR FLOW: A simple circular flow model of the macroeconomy containing two sectors (business and household) and two markets (product and factor) that illustrates the continuous movement of the payments for goods and services between producers and consumers. The payment flow between the two sectors and two markets is conveniently divided into four segments representing consumption expenditures, gross domestic product, factor payments, and national income. More advanced models containing additional flow segments are two-sector, three-market circular flow; three-sector, three-market circular flow; and four-sector, three-market circular flow. The two-sector, two-market circular flow model is the simplest way to show the inherent interrelationship between producers and consumers in the macroeconomy. It illustrates that actions by producers necessarily affect consumers and that actions by consumers necessarily affect producers. In particular, it illustrates that payments do not vanish from the macroeconomy, but are merely passed along. It shows that the expense of one sector is the revenue of another.Two Sectors, Two MarketsThe two macroeconomic sectors included in this model are:The two macroeconomic markets in this basic version of the circular flow are:Circulating Around| The Basic Circular Flow | 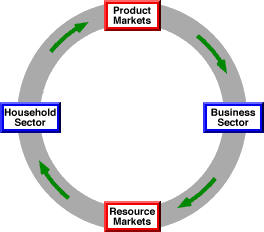 |
This diagram presents the simple two-sector, two-market circular flow. At the far left is the household sector containing people seeking consumption. At the far right is the business sector that does the production. At the top is the product markets that exchange final goods and services. At the bottom is the resource markets that exchange the services of the scarce resources.- Gross Domestic Product: Consider first the upper right-hand segment of the circular flow between the product markets and the business sector. This is the revenue received by the business sector for the production of goods and services, what is officially termed gross domestic product (GDP). Click the [Production] button to illustrate this flow.
- Factor Payments: Moving clockwise with the flow, the lower right hand segment between the business sector and the factor markets is factor payments. These are payments to the owners of labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurship for the productive services they provide. Factor payments can be divided into specific items depending on the resources involved, including wages, interest, rent, and profit. Click the [Factor Payments] button to illustrate this flow.
- National Income: Continuing clockwise to the lower left hand segment between the factor markets and the household sector is national income. Definitionally speaking this is the income earned by the factors of production, which are owned by the household sector. Click the [Income] button to illustrate this flow.
- Consumption Expenditures: The last segment of this flow, between the household sector and the product markets in the upper left hand corner, is consumption expenditures. These are expenditures made by the household sector for the purchase of gross domestic product. Click the [Consumption] button to illustrate this flow.
Circulating EqualityTwo points are worth emphasizing: - First, the flow between sectors and markets circulates. Gross domestic product is used for factor payments, which becomes national income, which is used for consumption expenditures, which buys gross domestic product, which is used for factor payments, which becomes national income, which is used for consumption, which is... And on it goes.
- Second, all four segments in this two-sector, two-market circular flow circular flow--gross domestic product, factor payments, national income, and consumption--are equal. The revenue received from selling gross domestic product is used for factor payments. The factor payments become national income. The national income is used for consumption. This consumption is then used to buy gross domestic product... And on it goes.
Other ModelsThis two-sector, two-market circular flow is a simple model of an exceedingly complex economy. More realistic and more complex models are available. The other models are:- Two Sectors, Three Markets: A second version of the circular flow model adds the financial market',500,400)">financial markets to the basic model. This addition illustrates how saving is diverted from the household sector to the business sector to finance investment expenditures.
- Three Sectors, Three Markets: A third version of the model includes the government sector. This model highlights the importance of taxes, which are also diverted from household sector income and used to finance government purchases.
- Four Sectors, Three Markets: The most comprehensive circular flow model includes the foreign sector. Adding the foreign sector highlights the role of trade with the rest of the world, especially exports and imports.

Recommended Citation:TWO-SECTOR, TWO-MARKET CIRCULAR FLOW, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: April 27, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BLUE PLACIDOLA
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time touring the new suburban shopping complex seeking to buy either throw pillows for your living room sofa or a hepa filter for your furnace. Be on the lookout for defective microphones.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
A scripophilist is one who collects rare stock and bond certificates, usually from extinct companies.
|

|
|
"Nothing is a waste of time if you use the experience wisely. " -- Auguste Rodin, Sculptor
|

|
SBA
Small Business Administration
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


